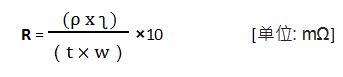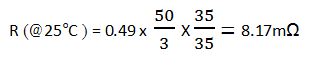Copper is a common conductive metal layer on the surface of a circuit board (PCB). Before estimating the resistance of copper on a PCB, please note that the resistance of copper varies with temperature. To estimate the resistance of copper on a PCB surface, the following formula can be used.
When calculating the general conductor resistance value R, the following formula can be used.
ʅ : conductor length [mm]
W: conductor width [mm]
t: conductor thickness [μm]
ρ : conductivity of conductor [μ ω cm]
The resistivity of copper is at 25°C, ρ (@ 25°C) = ~1.72μ ω cm
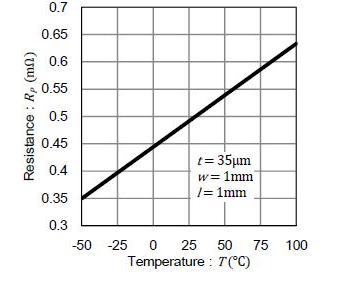
In addition, if you know the resistance of copper per unit area, Rp, at different temperatures (as shown in the figure below), you can use the following formula to estimate the resistance of the entire copper, R. Note that the dimensions of copper shown below are thickness (t) 35μm, width (w) 1mm, length (ʅ) 1mm.
Rp: resistance per unit area
ʅ : copper length [mm]
W: copper width [mm]
t: copper thickness [μm]
If the dimensions of copper are 3mm in width, 35μm in thickness and 50mm in length, the resistance value R of the copper at 25°C is
Thus, when 3A current flows copper on the PCB surface at 25°C, the voltage drops about 24.5mV. However, when the temperature rises to 100℃, the resistance value increases by 29% and the voltage drop becomes 31.6mV.
Post time: Nov-12-2021